Setup Speech Processor dependencies
Editor
Add a language model provider component to the scene.
If you want to load language model from StreamingAssets, add the
Streaming Assets Language Model Providercomponent. Specify the path to the language models relative to the StreamingAssets folder and select the default language from theLanguagepop-up menu.To add a new language model, download it (e.g. from here), extract it to the Unity StreamingAssets directory and specify path to its content and its language in
Streaming Assets Language Model Providersettings.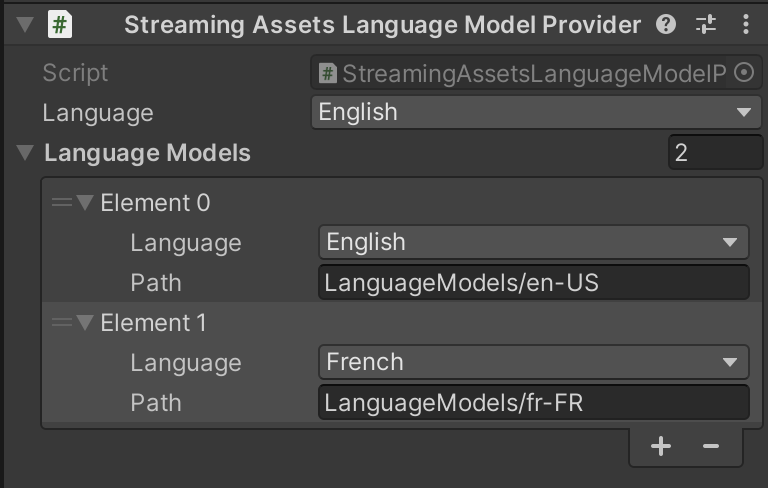
If you want to download remote zipped language model, add the
Remote Language Model Providercomponent. Specify the address of the remote zip containing language model files and select the default language from theLanguagepop-up menu. If the contents of the language model (foldersam,conf,graphetc.) are located in the root of the zip, leave theEntryfield empty, otherwise specify the path to the contents of the language model inside the zip.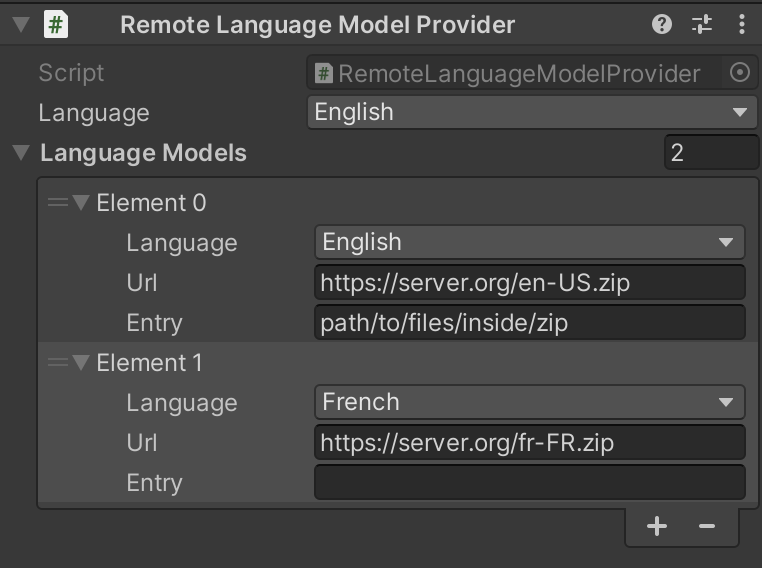
Add speech source component to the scene.
If you want to use microphone, add
Microphone Speech Sourcecomponent.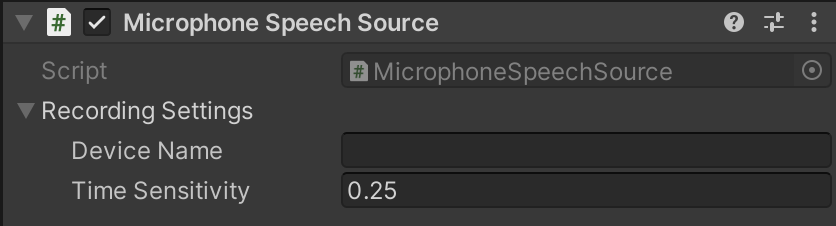
If you want to use audio clip, add
Audio Clip Speech Sourcecomponent and assign an audio clip to theClipfield. Use uncompressed mono audio (go to audioclip import settings and setForce To Monoto true,Load TypetoDecompress On Load).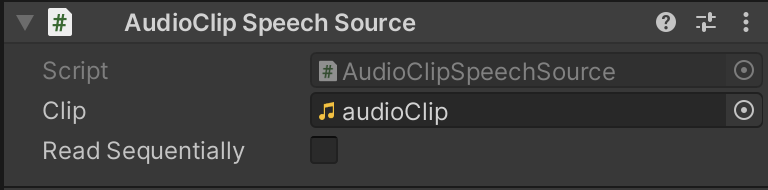
If you want to use AudioListener as a speech source, add
AudioListener Speech Sourcecomponent and specify channel from which you want the audio data to be streamed.
Explicit initialization
Speech processor implicitly initializes its dependencies when started. To initialize dependency explicitly, use SpeechProcessorDependency.Initialize() method. For example:
using System;
using System.Collections;
using Recognissimo;
using UnityEngine;
public class ExplicitInitializationExample : MonoBehaviour
{
// SpeechSource inherits SpeechProcessorDependency base class.
[SerializeField]
private SpeechSource speechSource;
private IEnumerator Start()
{
yield return speechSource.Initialize(HandleTaskStarted, HandleInitializationFail);
}
private void HandleTaskStarted(string taskName, bool isLongRunning)
{
// Print only for coroutines.
if (isLongRunning)
{
Debug.Log($"Starting task {taskName}");
}
}
private void HandleInitializationFail(string taskName, Exception exception)
{
Debug.Log($"Task {taskName} failed with error {exception.Message}");
}
}